Configure Default Numlock Mode
Quick Overview:The Numlock key on most standard keyboards toggles the numeric keypad between two different modes: (1) The Numeric Mode and (2) The Function Mode.
When the Numlock is turned "ON", the numeric keys on the keypad generate numbers, from 0 to 9. On the other hand, when Numlock is set to "OFF", these numeric keys generate other keystroke events such as "Home", "Page Up", "Page Down", etc...
Many versions of Windows by default, set Numlock key to "OFF", and this turns to be a bit annoying if you use that keypad regularly for numeric purposes. The good news is, you can always change this default behavior and set the Numlock key ON as default.
IMPORTANT This article will guide to some steps of modifying your Windows Registry. Stop if you're not familiar with the Windows Registry. Making an inappropriate change to the Windows Registry could cause critical problems to your computer.
Proceed at your own risks
- Open the "Registry Editor" ("Start" >> "Run", then type "regedit" and Enter).
- Expand to the following key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Keyboard - Here you should see a string value named "InitialKeyboardIndicators"
- Double-click on this name to popup the edit window
- Enter a desired numeric value under "Value Data" then click "Ok". Valid values are:
0: Numlock is OFF on startup
1: Disable Numlock Key
2: Numlock is ON on startup

















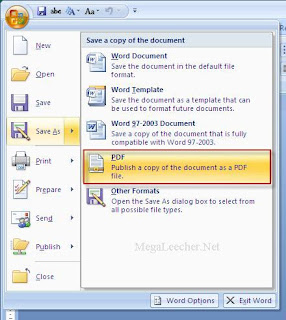
 , point to the arrow next to Save As, and then click PDF or XPS.
, point to the arrow next to Save As, and then click PDF or XPS.



